The rapid evolution of Meta's Llama models has marked a significant milestone in the AI landscape, with the recent releases of Llama 3.1 and 3.2 bringing groundbreaking improvements. As developers seek to harness these powerful models, understanding the key differences between Llama 3.1 and 3.2 becomes crucial for making informed implementation decisions. On Novita AI, we've observed how these advancements are reshaping AI development workflows and want to share a comprehensive analysis of both versions.
Understanding the Llama Model Family
The Llama family has evolved significantly since its inception, with each iteration bringing substantial improvements. Llama 3.1, released in July 2024, introduced the groundbreaking 405B parameter foundation model alongside 8B and 70B variants. These models supported eight languages, tool calling, and an expanded 128K context window.
The transition to Llama 3.2 marked another leap forward, primarily focusing on multimodal capabilities and accessibility. The new release maintained the core strengths of 3.1 while introducing vision-enabled 11B and 90B models, plus lightweight 1B and 3B variants for on-device applications.
Core Architecture and Technical Specifications
Llama 3.1 and 3.2 share fundamental architectural elements:
128K token vocabulary
128K context window
Support for eight languages
Native tool calling capabilities
Base and instruct versions
What's New About Llama 3.2
Llama 3.2's enhanced parameter counts (11B and 90B for multimodal models)
Introduction of lightweight models (1B and 3B)
Specialized vision-language cross-attention layers in 3.2
Optimized model architecture for multimodal processing
Developers can explore these capabilities firsthand through the LLM playground, where both versions can be tested without cost.
Multimodal Capabilities and Vision Features
Llama 3.2's most significant advancement is its multimodal architecture, which introduces:
Image object detection and scene understanding
OCR capabilities
Visual reasoning for equations and charts
Document analysis
Image captioning and visual Q&A
The vision integration follows a compositional approach:
Pre-trained image encoder
Pre-trained text model
Cross-attention layers connecting both components
Parallel processing of image and text inputs
Performance Benchmarks and Use Cases
Benchmark comparisons show:
Llama 3.1 405B achieving industry-leading performance in text-based tasks
Llama 3.2 multimodal models matching or exceeding competitors in vision-language tasks
Lightweight models maintaining competitive performance for their size class
Common use cases include:
Enterprise document processing
Visual content analysis
Multilingual support
On-device AI applications
Choosing Between Llama 3.1 and 3.2
When deciding between Llama 3.1 and 3.2, consider the following factors:
Task Requirements: If your application focuses solely on text-based tasks, Llama 3.1's 405B model might be the best choice. For multimodal applications involving image analysis, Llama 3.2's vision-enabled models are essential
Computational Resources: Llama 3.1's larger models require significant computational power. In contrast, Llama 3.2 offers lightweight options (1B and 3B) suitable for edge devices and mobile applications
Context Length: Both versions support an impressive 128K token context window, allowing for processing of lengthy documents or conversations
Multimodal Capabilities: If your project involves image reasoning, document analysis, or visual Q&A, Llama 3.2's multimodal models (11B and 90B) offer superior performance
Deployment Environment: Consider whether you need cloud-based solutions or on-device processing. Llama 3.2's lightweight models are optimized for edge deployment
Language Support: Both versions officially support eight languages, with the ability to fine-tune for additional languagesPerformance Benchmarks: Evaluate the specific benchmarks relevant to your use case. While Llama 3.1 excels in certain text-based tasks, Llama 3.2 shows improved performance in multimodal scenarios
How to Access Llama 3.1 and Llama 3.2 API on Novita AI
To access Llama 3 models on Novita AI, follow these steps:
Step 1:Choose your desired Llama 3 model:
For Llama 3.1
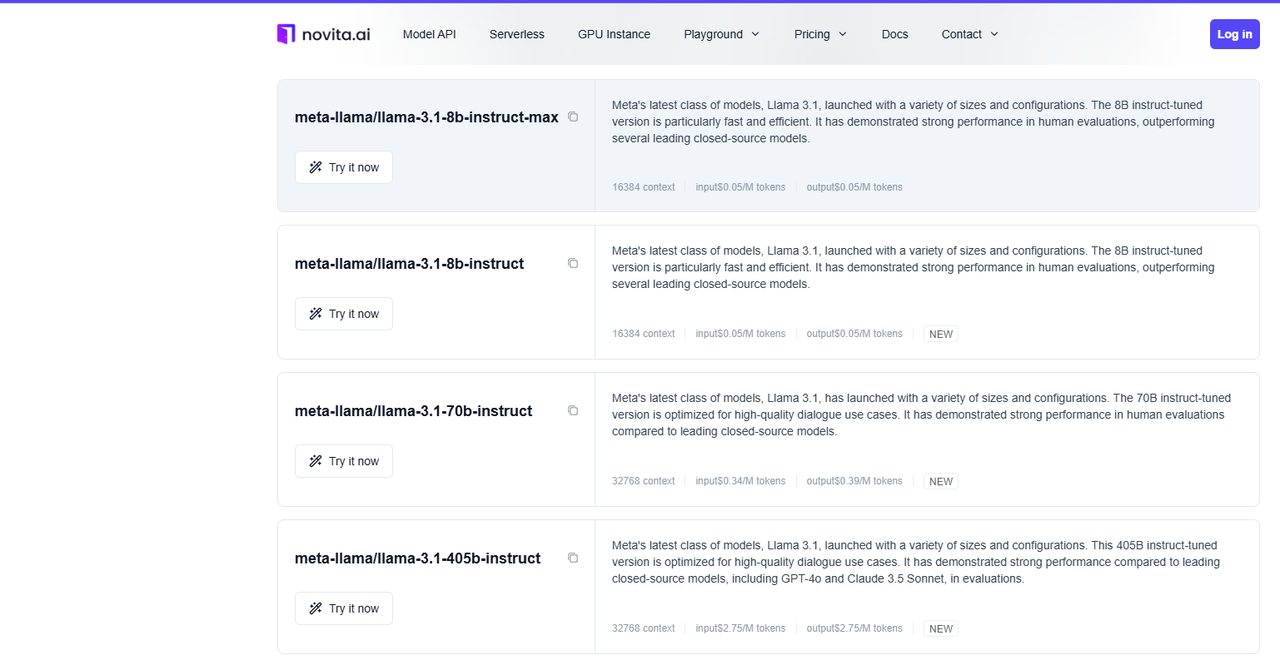
Llama 3.1 model list on Novita AI
For Llama 3.2:
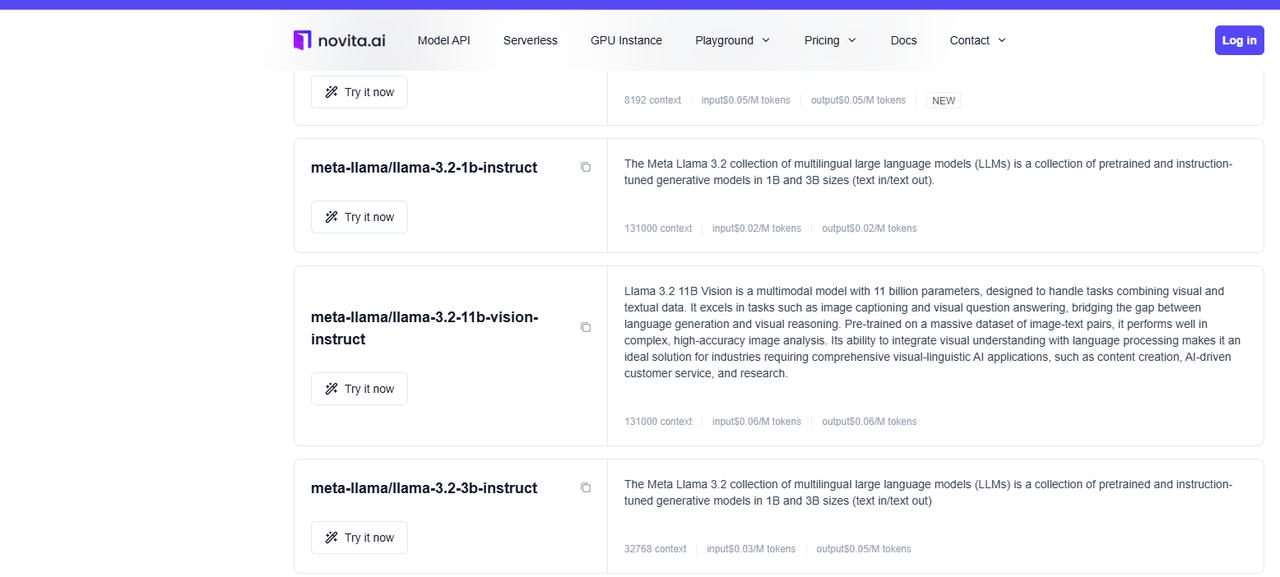
Step 2:Go to Novita AI and log in using your Google, GitHub account, or email address
Step 3:Manage your API Key:
Navigate to "Key Management" in the settings
A default key is created upon first login
Generate additional keys by clicking "+ Add New Key"
Explore the LLM API reference to discover available APIs and models
Step 4:Set up your development environment and configure options such as content, role, name, and prompt
Step 5:Run multiple tests to verify API performance and consistency
Novita AI provides a reliable, fast, and cost-effective platform with auto-scaling infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on application growth and customer service
Conclusion
The evolution from Llama 3.1 to 3.2 represents a significant advancement in AI model capabilities, particularly in multimodal processing and accessibility. While 3.1 excels in pure language tasks, 3.2's vision capabilities and lightweight options open new possibilities for AI applications. Developers should choose between them based on their specific use cases, resource constraints, and multimodal requirements.
Recommended Reading
Originally published at Novita AI
Novita AI is the All-in-one cloud platform that empowers your AI ambitions. Integrated APIs, serverless, GPU Instance — the cost-effective tools you need. Eliminate infrastructure, start free, and make your AI vision a reality.
